Chapter 1: Low Power Amplifiers
Sub
point: 1.2 Single stage CE amplifier,
frequency response, gain, bandwidth
Sub point:
1.3 Multistage amplifiers: General Multistage amplifier BJT based.
Sub point: 1.4 Type of BJT amplifier coupling: Circuit diagram, operation, frequency response
and applications of RC, transformer
and direct coupling
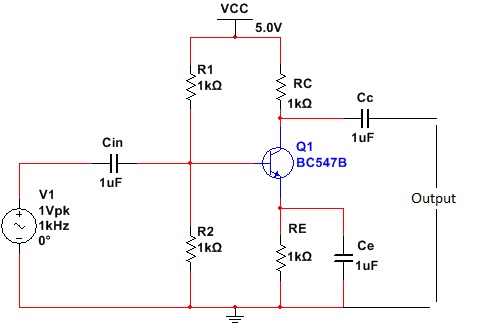
Figure:
Single stage CE amplifier
As we know,
amplifier is electronics circuit which is used to amplify weak signals and
basically transistors are used in amplifier circuits, let’s see the working of
single stage CE amplifier in which transistor is used as an amplifier (in
active region). Figure shows circuit diagram of single stage CE amplifier in
which 1 transistor, 4 resistors and 3 capacitors are used.
Functions of
components:
0) Transistor:
In active region transistor can be used as an amplifier (Collector-Base
junction (CB) reverse bias and Emitter-Base junction (EB) forward bias). The
property of transistor is to provide the phase shift of 1800, hence
the output of amplifier is out of phase to the input signal.
1) Resistors
R1 & R2: these resistors are used to provide voltage divider bias
arrangement so as to operate transistor in active region.
2) Resistor
Rc and Re: The output of circuit is taken across collector resistor Rc with
respect to the ground. The function of emitter resistor Re is to stabilize the
transistor. stabilization of transistor is necessary as it stabilizes the
operating point of transistor and make collector current Ic independent of
temperature changes. If transistor is not properly stabilized the there is
possibility of thermal runway (Thermal runway is the self destruction of unstabilized transistor.
3) Capacitors
Cin, Cc and Ce: The property of capacitor is to block DC quantities and pass AC
quantities. As amplifier is used to amplify AC i.e. analog signals, DC is
unwanted in the circuit, it is blocked by capacitor Cin. Coupling capacitor is
used to couple output of first stage to next stage. Emitter capacitor is used
to provide low reluctance path to amplified signals.
Figure: Frequency response of
RC coupled amplifier
Bandwidth: It is the range over which the output
of circuit is satisfactory.
Multistage
amplifiers:
|
|
|
|
Figure:
Multistage amplifier
- Amplifier couplings:
As in
previous section, we have seen need of multistage amplifiers, in this section,
we will see different types of coupling.
·
What are different types of amplifier
coupling?
The different types of cascading
(coupling) are as follows:
1. R-C coupled amplifier
2. Transformer coupled amplifier
3. Direct coupled amplifier
- R-C coupled amplifier:
RC coupled amplifier is generally used
type of coupling among the available methods. It is mostly used for voltage
amplification.
Figure: Two stage RC coupled
amplifier
Figure shows RC coupled amplifier in which
output of first stage is coupled to the next stage by using RC (Hence called as
RC coupled amplifier). A coupling capacitor Cc us used to
connect the output of first stage of amplifier to the next stage and so on. The
resistance R1, R2 forms the voltage divider biasing and resistor Re is used to
stabilization of transistor. The emitter capacitor (also known as bypass
capacitor) Ce is used to provide low reactance path to the signal. The coupling
capacitor Ce passes ac signal and blocks dc which avoids DC interference in the
circuit. When ac signal is applied to the base of the first transistor, we get
amplified output across collector load RC which is given to the base of next
stage by using coupling capacitor Cc. Now 2nd stage performs further
amplification of the signal and in this way the cascaded (in series) stage
amplify and overall gain is considerably increased.
Frequency
response of RC coupled amplifiers:
Figure:
Frequency response of two stage RC coupled amplifier
From frequency response curve of RC
coupled amplifier, it is clear that bandwidth is large. Voltage gain reduces at
low frequencies (50 hz) and high frequencies (20 khz) but remains constant over
mid frequency range (50 hz, to 20 khz).
Advantages of RC coupled
amplifier:
1)
Excellent frequency response
2)
Gain is constant over audio
frequency
3)
It is less costly
Disadvantages of RC coupled
amplifier:
1)
It have low voltage gain and power
gain.
2)
Due to aging effect, it becomes
noisy
Applications of RC coupled
amplifier:
1)
It is mainly used in audio
amplifier (pre-amplifiers)
- Transformer coupled amplifier
Figure shows transformer coupled
amplifier in which output of first stage is coupled to the next stage by using
transformer (hence called as transformer coupled amplifier).
Transformer coupling is generally used
when the load is small. It is mostly used for power amplification. In above fig
a coupling transformer is used to couple the output of one stage to the input
of the next stage.
The Primary winding of transformer is used
as the collector load and its secondary winding is used to couple the output of
first stage to the next stage. When ac signal is applied to the base of first
stage , it appears in the amplified form across primary winding of the coupling
transformer and the voltage developed across primary is transferred to the
input of the next stage by the transformer secondary.
Frequency
Response of Transformer coupled amplifiers:
Figure: Frequency response of transformer coupled amplifier
From the frequency response of transformer
coupled amplifier, it is clear that the frequency response is very poor in
which gain remains constant only over a small range of frequency and will
change with change in frequency.
Excellent impedance matching is achieved
with transformer coupling?
Yes, transformer coupled amplifiers are used to provide excellent
impedance matching between the individual stages. To match the load impedance, a step-down
transformer of proper turn’s ratio is used. The resistance of the secondary
winding of the transformer is made equal to the loads impedance, and primary
winding is made equal to the output resistance of the amplifier.
Advantages of transformer
coupled amplifier:
1)
No signal power loss
2)
Excellent impedance matching
Disadvantages of a transformer
coupled amplifier:
1)
Poor frequency response
2)
Gain varies with the varying
frequency
3)
Bulky transformers are used hence
circuit is bulky
4)
Transformers creates noise
5)
High distortion in the frequency
Application of transformer
coupled amplifier:
1)
Used in impedance matching circuits
2)
Used as power amplifier in last
stage
- Direct coupled amplifier:
Figure: Direct coupled amplifier
Figure
shows direct coupled amplifier in which output of first stage is connected to
the next stage directly without using any coupling circuit (hence called as
direct coupled amplifier)
Direct
coupled amplifiers are used to amplify extremely low frequencies like
photocurrent, thermocouple current etc. generally complementary transistors are
used in the circuit like first stage uses NPN transistor then second stage uses
PNP transistor and so on, which makes circuit stable with respect to the
changes in temperature.
The
signal to be amplify is given to the base of first stage transistor. Due to
transistor action signal gets amplified and appears across the collector
resistor Rc which is then given to the next stage.
Frequency response of of
direct coupled amplifier:
Figure: Frequency response of of direct coupled amplifier
Advantages of direct coupled
amplifier:
1)
Circuit is simple
2)
Cost is less
3)
Small in size
Disadvantages of direct
coupled amplifier:
1)
It cannot be used to amplify high
frequencies
2)
Operating point of transistor
changes due to change in temperature
Applications of direct coupled
amplifier:
1)
To amplify extremely low
frequencies like photocurrent.
- Difference between amplifier coupling techniques
Parameter
|
RC coupling
|
Transformer
coupling
|
Direct
coupling
|
Type of
coupling used
|
RC coupling
|
Transformer
|
direct
|
Frequency
response
|
Excellent
|
Poor
|
Best
|
Frequency
response curve
|
|||
Cost
|
Less
|
More
|
Very less
|
Space and
weight
|
Less
|
More
|
Very less
|
Impedance
matching
|
Poor
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Gain
|
Less overall
voltage gain
|
High voltage
gain
|
Uniform voltage
gain upto certain frequencies
|
Application
|
Voltage amplifier,
audio amplifier in prior stage
|
Power amplifier,
last stage of audio amplifier
|
Low frequencies
applications
|













No comments:
Post a Comment